US AI Policy: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Comply in 2026
Explore how the 2025 US AI Policy shapes innovation, safety, and compliance. Learn about Executive Order 14110, NIST AI RMF, OMB guidance, and real-world business impacts.
Visual representation of USA AI Policies showing collaboration between humans and artificial intelligence under U.S. regulatory frameworks.
If you lead, build, or deploy AI systems in the United States, US AI policy now touches everything from your model testing and disclosures to vendor management, data governance, and incident response. In 2025, the landscape blends federal executive actions, NIST standards and guidance, emerging agency rules, and intense state-level activity—with new proposals in Congress that could reshape preemption and enforcement.
This guide distills what matters most right now, maps the practical implications for organizations, and offers a step-by-step approach to operationalizing compliance without slowing innovation.
The Core Building Blocks of US AI Policy
1) The 2023 Executive Order—and its 2026 afterlife
In late 2023, Executive Order 14110 (“Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of AI”) set a sweeping agenda for AI safety standards, developer responsibilities, and federal procurement and oversight. It directed agencies to issue guidance, testing standards, and reporting requirements, while tasking the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to expand measurement and evaluation work.
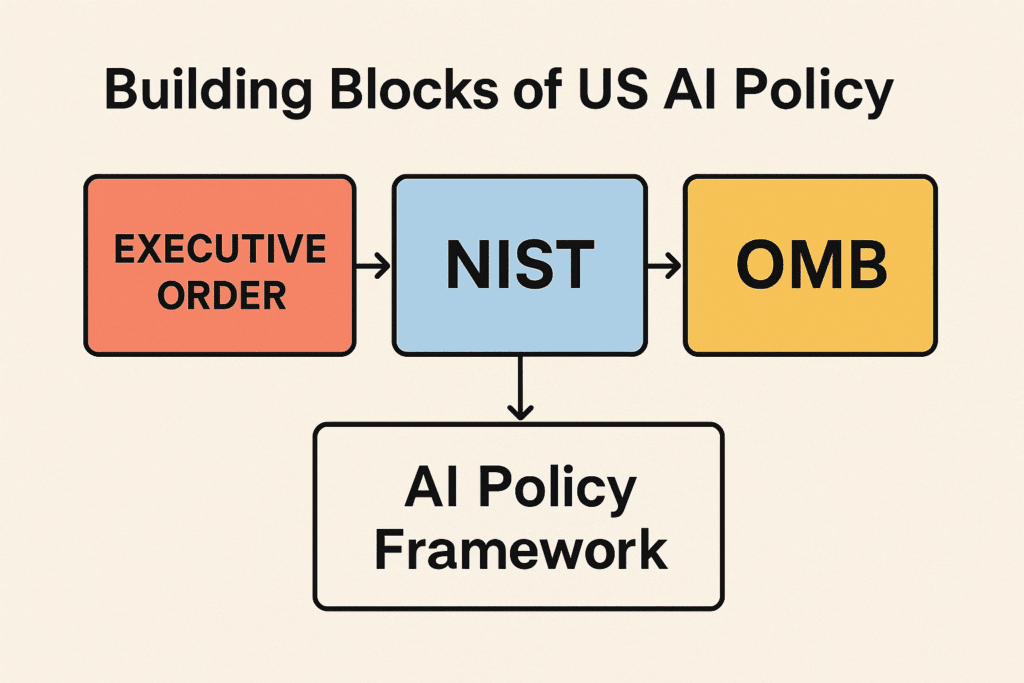
In 2025, reporting has highlighted attempts to unwind portions of that framework, including a reported rescission of the 2023 order. The policy signal to industry: expect contention and flux at the federal level, with elements likely to persist through agencies, standards bodies, and procurement even as formal directives shift. The Verge
2) OMB’s government-wide rules for federal AI use
The Office of Management and Budget issued M-24-10 in March 2024, instructing agencies on governance, risk management, inventories of AI use cases, and safeguards for safety-impacting systems. For vendors, that means federal buyers increasingly expect documentation, testing artifacts, and risk mitigations aligned to OMB guidance. White House+1
3) NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF)
NIST’s AI RMF 1.0 is the de facto blueprint for many U.S. organizations. It is voluntary, risk-based, and designed to be sector-agnostic, with a playbook and resource center that help teams translate principles into controls, processes, and metrics. Expect regulators, auditors, and large customers to ask how your AI program maps to it. NIST+2NIST+2
4) The U.S. AI Safety Institute (AISI) and the AISI Consortium
Housed within NIST, AISI and its consortium of 280+ organizations are building methods to evaluate advanced models, document capabilities and risks, and standardize safety testing. Public MoUs with leading labs to enable earlier model access for evaluation underscore where testing norms are headed. NIST+2Reuters+2
5) Congress, states, and global context
Congress is debating bills ranging from deepfake takedowns to research infrastructure. Meanwhile, states (e.g., New York City’s bias-audit rule for hiring tools, California proposals on “frontier” model safety) continue to act. Globally, the EU AI Act and a 2024 UN AI resolution set expectations U.S. firms can’t ignore if they operate internationally. Reuters+3Congress.gov+3Wikipedia+3
Further reading:
• Wikipedia overview of Regulation of AI in the United States
• Forbes analysis on the policy pivot from “safety” to “security”: US AI Policy Pivots Sharply From ‘Safety’ To ‘Security’
What US AI Policy Means for Your Organization
Procurement & customer expectations
Large enterprises, agencies, and regulated sectors increasingly require AI risk artifacts: model and data lineage, pre-deployment testing reports (including red-team results where applicable), monitoring plans, incident response runbooks, and governance attestations aligned to NIST AI RMF and OMB language. If you sell into the federal government, expect M-24-10-informed questionnaires and contract clauses. White House
Model development & evaluation
The direction of travel is clear: measure, test, and document. Even if executive actions ebb and flow, AISI and NIST are standardizing evaluation baselines—capabilities, safety hazards, misuse vectors (e.g., bio, cyber), and model reporting. Early participation pays off: the closer your evaluation practice is to NIST/AISI methods, the easier external reviews become. NIST
HR, hiring, and discrimination risk
State and local rules (like NYC’s AEDT bias-audit requirement) and federal civil-rights enforcement mean teams must track fairness, transparency, and explainability for AI used in hiring, lending, housing, and benefits decisions. Expect requests for independent bias audits, clear disclosures, and candidate notices where required. (See the NYC rule and related agency compliance examples.) Wikipedia+1
International obligations
U.S. companies serving the EU will face risk-tiering, transparency, and oversight obligations under the EU AI Act. Many U.S. firms choose to “baseline to the strictest regime” to reduce fragmentation—often mapping EU requirements to NIST AI RMF controls and internal policies. Investopedia
A Practical, 7-Step Compliance Playbook (Without Killing Velocity)
Step 1: Establish AI governance with owners and thresholds
Create a cross-functional AI Governance Council (product, security, legal, risk, ethics, HR). Define risk thresholds (e.g., what counts as “safety-impacting”), an approval workflow, and documentation requirements aligned to NIST AI RMF functions (Map → Measure → Manage → Govern). NIST
Step 2: Build an AI use-case inventory
Maintain a living inventory covering models, data sources, third-party tools, and use-case risk levels. Track whether each use case triggers special safeguards (e.g., for consequential decisions in employment or credit). Federal contractors should mirror OMB M-24-10 inventory expectations for smoother procurement. White House
Step 3: Formalize model lifecycle controls
Adopt an ML Ops + Risk checklist: data provenance, privacy controls, synthetic data use, evaluation protocols, red-team plans, and change management for new releases. Keep a Model Card (or equivalent) with risks, mitigations, and monitoring KPIs. Align terminology and checkpoints with AISI/NIST drafts to future-proof. NIST
Step 4: Pre-deployment testing and third-party reviews
For medium/high-risk systems, run adversarial testing (jailbreaks, prompt-injection, data exfil), safety hazard probes (bio/cyber misuse where relevant), and fairness/bias evaluations. Where required by customers or regulators, commission independent audits and bias testing—especially for hiring and lending flows. Wikipedia
Step 5: Human oversight, documentation, and disclosures
Document intended use, limitations, and fallbacks (human appeal channels). Provide user-facing notices when AI materially influences outcomes. Build explanations appropriate to the task and audience (e.g., adverse action notices in finance; candidate notices in hiring).
Step 6: Continuous monitoring and incident response
Instrument production with telemetry for drift, harmful output, policy violations, and model degradation. Define severity tiers and playbooks for model rollbacks, content filters, and retraining triggers. Maintain an AI incident register that captures root cause and corrective actions.
Step 7: Contracts and vendor management
Bake AI obligations into DPAs and MSAs: evaluation rights, audit cooperation, disclosure duties for fine-tuning and training data, and sub-processor transparency. Require vendors to map to NIST AI RMF and provide testing summaries on request. NIST
Want a deeper dive on governance templates, model cards, or audit checklists?
See AI Risk Toolkit and AI Vendor Due Diligence Checklist.
Policy Trendlines to Watch in 2026
- Federal vs. state preemption. Some proposals would limit states’ ability to regulate AI—a pivotal determinant of whether U.S. compliance stays fragmented or converges on federal baselines. The Guardian
- From “safety” to “security.” Commentators note a pivot in emphasis from broad safety and rights protections toward national security, competitiveness, and rapid deployment, with practical consequences for priorities and funding. Forbes
- Standards-first enforcement. Even amid political shifts, NIST/AISI methods are likely to shape audits, procurement, and litigation discovery (what you tested, when, and with what rigor). NIST
- Global interoperability. With the EU AI Act moving toward full effect, U.S. multinationals will harmonize controls across NIST, EU, and sectoral rules—similar to the GDPR effect in privacy. Investopedia
Implementation Checklist (Copy/Paste)
- Name an AI Product Owner for each use case; set risk tiers and approval gates.
- Map to NIST AI RMF; choose controls you’ll operationalize in 90 days vs. 12 months. NIST
- Inventory all AI (internal and vendor) with purpose, data, model lineage, and risk. White House
- Define testing batteries: capability evals, safety hazards, bias/fairness, and red-teaming. NIST
- Ship documentation: Model Cards, user notices, fallback procedures, appeal channels.
- Monitor in production for drift/harm; run tabletop incident simulations quarterly.
- Update contracts: disclosure, audit cooperation, and sub-vendor transparency clauses.
Need templates? Check AI Governance Framework Template and Model Evaluation Plan.
External Resources and Further Reading
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework (overview and downloads). NIST.
- OMB M-24-10 memo for federal AI governance. White House
- NIST AI Safety Institute & Consortium updates. NIST
- Congressional Research Service brief on U.S. & international approaches. Congress.gov
- EU AI Act overview for cross-border operations. Investopedia
Also see: What Is Artificial Intelligence? (Wikipedia) for foundational context, and Sen. Schumer’s SAFE Innovation framework speech (CSIS) for legislative direction-of-travel. CSIS
FAQs About US AI Policy
1) What is US AI policy, and who enforces it?
US AI policy currently combines federal executive actions (e.g., EO 14110), agency guidance (e.g., OMB M-24-10), voluntary standards (NIST AI RMF), sectoral laws, and state/local rules. Enforcement flows through existing regulators (FTC, EEOC, CFPB, state AGs), procurement requirements, and—where applicable—state statutes and city ordinances.
2) How does US AI policy affect small and mid-sized businesses?
SMBs increasingly face customer-driven requirements: risk documentation, testing summaries, and model transparency—especially when selling into enterprises or government. Mapping a lightweight program to NIST AI RMF and adopting clear vendor due-diligence processes is often the most efficient path. NIST
3) Do I need to follow NIST AI RMF even if it’s “voluntary”?
While voluntary, NIST AI RMF is rapidly becoming the common language for auditors, customers, and agencies. Aligning to it reduces friction in sales cycles and helps future-proof against evolving rules. NIST
4) What’s the difference between US AI safety and security priorities?
“Safety” focuses on harms to people and society (bias, misinformation, dangerous capabilities), while “security” emphasizes national competitiveness, defense, and resilience. Current debates suggest a shift toward security framing in 2025, but both lenses matter for compliance and reputation. Forbes
5) How do EU rules intersect with US AI policy?
If you operate in or sell to the EU, you’ll need to comply with the EU AI Act. Many U.S. firms choose to standardize on NIST AI RMF internally and then map to EU AI Act obligations to avoid duplicative controls. Investopedia
Bottom Line
Even amid political shifts, the operational core of US AI policy is settling around risk management, testing, transparency, and documentation. Align to NIST AI RMF, prepare OMB-style inventories and safeguards if you work with agencies, and track AISI evaluation methods. That’s how to stay compliant and ship great AI products.
Looking for help getting started? Explore AI Program Quick-Start or Responsible AI Policy for Product Teams.


1 thought on “US AI Policy: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Comply in 2026”