Sensitive Data: What It Means, Why It Matters & How to Protect It 2025
Sensitive data is confidential information that, if exposed, threatens privacy, finances & security. Learn what counts — and how to safeguard it.

Protecting sensitive data is crucial in the digital age.
Sensitive data is confidential information that, if exposed, threatens privacy, finances & security. Learn what counts — and how to safeguard it.
Sensitive Data: What It Means, Why It Matters & How to Protect It.
Introduction
In today’s digital age, organizations and individuals alike generate and store massive amounts of information — from personal health records to financial transactions, from login credentials to corporate trade secrets. Among this sea of data, some information is especially critical. This is sensitive data — information that, if exposed or misused, can cause serious harm: identity theft, financial loss, privacy breaches, reputational damage, or even legal consequences.
Protecting sensitive data is no longer optional. With cyber‑attacks, data leaks, and regulatory fines on the rise, businesses and users must know what qualifies as sensitive data — and implement strong defenses. In this article, we explore the definition, types, real risks, and proven strategies to safeguard sensitive data in 2025 and beyond.
What Is “Sensitive Data”? — Definition and Categories
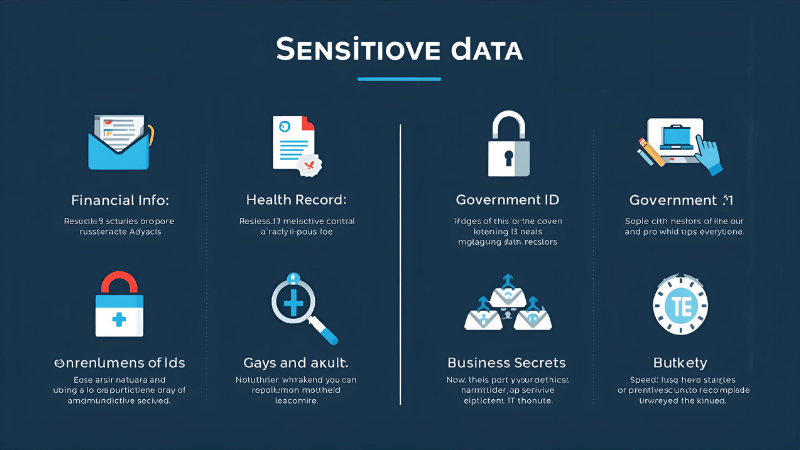
Sensitive data refers to any information that must be protected from unauthorized access or disclosure because of its confidential or private nature.
Personal vs. Sensitive Data – What’s the Difference?
Not all personal data is necessarily sensitive. For instance, a name or job title might be public or lightly protected. Sensitive data often includes personally identifiable information (PII) — but goes further, encompassing data that could cause serious harm if exposed.
Common categories of sensitive data include:
Financial information (bank accounts, credit card numbers, payment data)
Health and medical records (including protected health information, lab results, biometric data)
Authentication credentials (passwords, keys, secure tokens) and security-related identifiers
Government‑issued identifiers (social security numbers, national IDs, passport numbers, driver’s licenses)
Confidential business or corporate data (trade secrets, intellectual property, proprietary data)
Sensitive personal attributes (ethnic origin, health status, political or religious beliefs, biometric information) — depending on jurisdiction and legal definitions.
Because of its high risk profile, sensitive data typically requires stricter handling and security measures compared to general public or less‑critical data.
Why Sensitive Data Matters — Risks and Consequences of Exposure
When sensitive data is breached, the impact can be severe — for individuals, businesses, and even society at large.
Financial, Privacy & Reputational Damage
Identity theft & fraud: Exposed financial or personal identifiers can be used for fraudulent transactions or identity theft.
Legal and regulatory consequences: Many regions enforce strict privacy laws (e.g. HIPAA for health data, GDPR for personal data) — failure to protect sensitive data can lead to significant fines and legal liability.
Business impact: Data breaches often result in lost customer trust, reputational harm, brand damage — and sometimes long-term business decline.
Organizational Risks & Broader Implications
- Data breaches and leaks: In recent years, the frequency of data breaches has surged. For example, 2025 saw a dramatic rise in recorded incidents globally.
- High cost of breach: The global average cost of a data breach remains in the multi‑million‑dollar range (over $4–5 million on average) depending on industry and scale.
- Cascade effects: When sensitive data from one domain (e.g. healthcare or supply chain) leaks, it can trigger larger systemic risks — especially when combined with other compromised systems or interlinked infrastructures.
These stakes make it crucial for organizations and individuals to treat sensitive data with the highest level of protection.
Common Sources of Sensitive Data Exposure

Understanding how sensitive data leaks or gets exposed is key to preventing breaches. Common sources and vectors include:
- Human error & negligence: Misconfigured servers, weak passwords, or accidental sharing of sensitive files.
- Malware, phishing & credential theft: Attackers often exploit stolen credentials, phishing attacks, or malware to gain unauthorized access.
- Poor encryption / inadequate access controls: Data stored without proper encryption or with insufficient authentication is at high risk.
- Supply‑chain vulnerabilities & third‑party integrations: When multiple vendors, SaaS tools or external partners process or access sensitive data, weak links can expose the data.
- Legacy systems and unpatched software: Older or unmaintained systems may have vulnerabilities, making sensitive data easier to breach.
Best Practices & Strategies to Protect Sensitive Data
Protecting sensitive data requires a comprehensive, layered approach — combining people, processes, and technology.
Data Classification & Access Controls
Classify your data according to sensitivity: public, internal, confidential, restricted/sensitive. This helps prioritize protection.
Enforce least-privilege access — ensure only authorized users and systems can access sensitive data.
Use strong authentication (e.g. multi-factor authentication), robust identity management, and secure credential storage.
Encryption & Secure Storage
Encrypt sensitive data both at rest (storage) and in transit (network communication).
Use secure, modern encryption standards — avoid outdated or weak algorithms.
For highly sensitive data (financial, health, credentials), consider additional safeguards like hardware-based encryption, tokenization, or secure vaults.
Monitoring, Logging & Anomaly Detection (AI‑Enabled)
Maintain detailed logs for access events, changes, system actions — so any unauthorized access can be detected and audited.
Use anomaly detection tools (including AI/ML‑based monitoring) to spot unusual behavior — e.g. unexpected data downloads, access from unknown IPs, or bulk file transfers.
Regular audits and vulnerability scans — ensure systems remain secure over time.
Employee Awareness, Policies & Regular Training
Human error is one of the biggest causes of data exposure — conduct regular staff training on secure data handling, phishing risks, password hygiene.
Implement clear data handling, classification, and compliance policies.
Restrict access and privileges based on roles; enforce least privilege and separation of duties.
Vendor & Third‑Party Risk Management
Audit and vet third‑party vendors or SaaS providers before granting access to sensitive data.
Require compliance with security standards (e.g. GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001) where applicable.
Use data‑processing agreements and enforce secure data handling for external partners.
visit more like this.
Role of AI & Automation in Enhancing Sensitive Data Security
As cyber‑threats evolve, AI and automation tools have become powerful allies in safeguarding sensitive data.
- AI-based threat detection: Machine-learning models can analyze large volumes of logs and user behavior to detect anomalies or suspicious activity that may indicate a breach or insider threat.
- Automated encryption and key management: Modern tools help enforce encryption standards, rotate keys, and manage credentials without relying solely on manual processes.
- Automated compliance and audit workflows: AI-driven compliance tools can flag noncompliant data handling, missing logs, or misconfigured permissions — reducing human oversight burdens.
- Proactive vulnerability detection: Automated scans, AI-based vulnerability assessment in legacy systems, and predictive risk modeling help organizations stay ahead of threats.
By combining human vigilance with AI-powered tools, businesses can build a robust defense posture for sensitive data — a crucial step given the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks.
If you’re interested in exploring AI-based solutions and cybersecurity tools, you might also like our other resources under the Cybersecurity & AI section of this site.
Conclusion — Treat Sensitive Data as a Strategic Asset
Sensitive data is not just another type of information — it is often the most critical asset an individual or organization holds. Whether it’s someone’s financial details, health records, business secrets, or authentication credentials, exposure can wreak havoc on privacy, finances, reputation, and trust.
In 2025’s threat landscape — with rising data breaches, credential theft, supply‑chain vulnerabilities, and increasingly sophisticated attackers — protecting sensitive data is more important than ever.
By understanding what qualifies as sensitive data, recognizing the main sources of risk, and adopting a layered, proactive security approach (encryption, classification, monitoring, training, vendor management, and AI-driven automation), you can significantly reduce the chances of exposure and safeguard both individuals and organizations.
Use this guide as your foundation — then build tailored policies, invest in secure systems, and make data protection a priority.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is considered sensitive data?
Sensitive data includes any information that, if exposed or accessed by unauthorized parties, could lead to identity theft, financial loss, privacy violation, or legal consequences — such as financial records, health data, personal identifiers, credentials, and proprietary business data.
What are the most common ways sensitive data gets exposed?
Common exposure sources include human error (misconfiguration, accidental sharing), phishing and credential theft, unencrypted storage or insecure configurations, weak access controls, and vulnerabilities in third‑party services or legacy systems.
How can organizations protect sensitive data effectively?
Effective protection involves classifying data, enforcing access controls, using strong encryption, implementing multi-factor authentication, monitoring systems and logs, conducting regular audits, training employees, and managing third‑party/vendor risks.
Can AI help secure sensitive data?
Yes — AI and automation tools can significantly enhance data security through anomaly detection, automated encryption and key management, vulnerability scanning, compliance monitoring, and proactive threat detection.
What happens if sensitive data is breached?
A data breach involving sensitive data can cause severe consequences: identity theft, financial losses, regulatory fines, reputational damage, loss of customer trust — depending on the scope and nature of the data exposed.
For more blogs like this, visit this page: