Robotic Process Automation in Finance and Accounting: How RPA Is Transforming Financial Operations in 2026
Discover how robotic process automation in finance and accounting boosts efficiency, accuracy, and compliance with intelligent automation tools.

Discover how robotic process automation in finance and accounting boosts efficiency, accuracy, and compliance with intelligent automation tools.

Robotic Process Automation in Finance and Accounting
In today’s fast-changing digital landscape, robotic process automation in finance and accounting (RPA) has become a powerful tool for streamlining manual financial tasks, improving accuracy, and reducing costs.
Financial institutions are embracing process automation in finance to handle high-volume, repetitive processes such as data entry, reconciliation, and reporting — freeing up professionals to focus on strategic decision-making.
According to Forbes, automation technologies like RPA and intelligent automation are driving the next major leap in business efficiency across industries, especially in financial services.
What Is Robotic Process Automation in Finance?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to the use of software robots or “bots” that mimic human actions to complete rule-based tasks.
In finance, this means automating everyday processes like invoice management, financial reporting, and compliance checks.
Automation in Finance Meaning
In simple words, automation in finance means using digital tools — such as RPA, AI, and data analytics — to perform routine operations faster and more accurately than humans could manually.
For example, RPA can automatically extract data from invoices, match payments, and update ledgers in ERP systems — all without human error.
Key Benefits of RPA in Finance and Accounting
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Compliance
Finance teams deal with complex, regulation-heavy data. RPA reduces manual data entry errors and ensures every process follows pre-set compliance rules.
This helps organizations align with strict financial regulations like Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) and Basel III.
2. Time and Cost Efficiency
By automating repetitive processes, RPA allows finance teams to complete tasks 60–70% faster.
A study by Deloitte found that organizations implementing RPA in finance experience ROI within 12 months.
3. Better Financial Reporting
Automated reporting in finance eliminates delays and inconsistencies that occur with manual reporting.
Bots can instantly compile data from multiple systems, prepare balance sheets, and generate detailed financial statements — saving valuable hours each month.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
RPA tools can easily scale with business growth. When transaction volumes increase during fiscal year-ends or audits, automation can handle the load without adding staff.
5. Data Security and Audit Trails
Every action performed by a software bot is recorded. This creates a transparent and secure audit trail — critical for financial governance and internal controls.
Popular Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation in Finance
1. Accounts Payable (AP) Automation
RPA automates invoice validation, payment scheduling, and vendor reconciliations — reducing human involvement and fraud risk.
2. Financial Reporting
Automated bots gather and validate data from different systems to produce accurate financial reports.
For example, monthly close processes can be shortened from days to hours.
3. Payroll and Expense Management
HR and finance teams benefit from automated payroll validation, tax deductions, and employee expense reporting.
4. Risk and Compliance Monitoring
With intelligent automation in finance, companies can continuously monitor transactions for compliance breaches or unusual activity.
5. Customer Onboarding and KYC
Banks and fintechs use RPA to automate Know Your Customer (KYC) checks — a time-consuming, error-prone process that becomes faster and more reliable with automation.
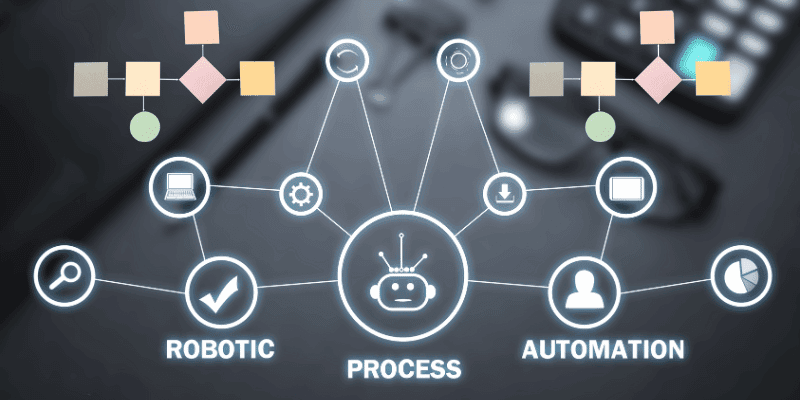
Example of how robotic process automation streamlines financial tasks like data entry, reporting, and compliance monitoring.
RPA and Intelligent Automation in Finance
While RPA handles structured, rule-based tasks, intelligent automation (IA) takes things further.
IA combines machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and AI to make smart decisions and adapt to unstructured data.
This means automation in finance is evolving from simple data processing to cognitive automation — capable of interpreting invoices, analyzing patterns, and predicting financial outcomes.
Challenges in Implementing RPA
Despite its advantages, adopting robotic process automation in finance can come with some challenges:
- Integration Issues: RPA must connect seamlessly with legacy ERP systems.
- Change Management: Employees may resist automation fearing job loss.
- Process Standardization: Automation works best on standardized workflows — requiring process optimization first.
- Regulatory Oversight: Compliance with AI and data protection laws (like GDPR or the upcoming U.S. AI Policy 2025) is crucial.
Regulatory Context: AI, RPA, and Compliance
The growing reliance on automation has attracted global regulatory attention.
Governments are now outlining frameworks to ensure AI and automation are transparent, accountable, and ethical.
Stay informed about these evolving policies through our detailed guides on:
Both policies emphasize responsible AI governance, which directly affects automation tools used in fintech and banking.
The Future of Automation in Finance
The next decade will witness the rise of hyperautomation — integrating RPA, AI, and data analytics into one unified ecosystem.
Financial institutions will transition from automating single tasks to end-to-end financial processes, such as real-time compliance monitoring and AI-driven forecasting.
Leading banks and fintech firms are already investing in intelligent automation platforms like UiPath, Blue Prism, and Automation Anywhere to drive efficiency and innovation.
According to Wikipedia, RPA adoption is expected to grow by over 50% in the financial sector by 2026.
Conclusion
Robotic process automation in finance and accounting is no longer optional — it’s essential for competitiveness, compliance, and scalability.
Organizations that embrace automation early are better positioned to adapt to digital transformation and shifting regulatory landscapes.
As AI and RPA continue to merge, finance professionals will move from manual data handling to strategic, data-driven decision-making.
The future of finance is intelligent, automated, and faster than ever.
Explore more insights on AI in Finance / Fintech for expert updates on digital transformation in financial services.
FAQs About Robotic Process Automation in Finance
1. What is robotic process automation in finance and accounting?
It refers to using software bots to automate repetitive financial tasks such as invoicing, reporting, and reconciliations, improving efficiency and compliance.
2. How is robotic process automation used in finance?
RPA automates routine operations like accounts payable, financial reporting, and data entry, saving time and reducing manual errors.
3. What are the benefits of process automation in finance?
It enhances accuracy, speeds up workflows, ensures compliance, and allows finance professionals to focus on strategic analysis.
4. What is intelligent automation in finance?
Intelligent automation combines RPA with AI technologies like machine learning to make smarter, adaptive financial processes.
5. Is automation in finance safe and compliant with regulations?
Yes, when implemented properly. It helps organizations maintain audit trails, ensure data accuracy, and comply with global regulations such as the EU AI Act and U.S. AI Policy.